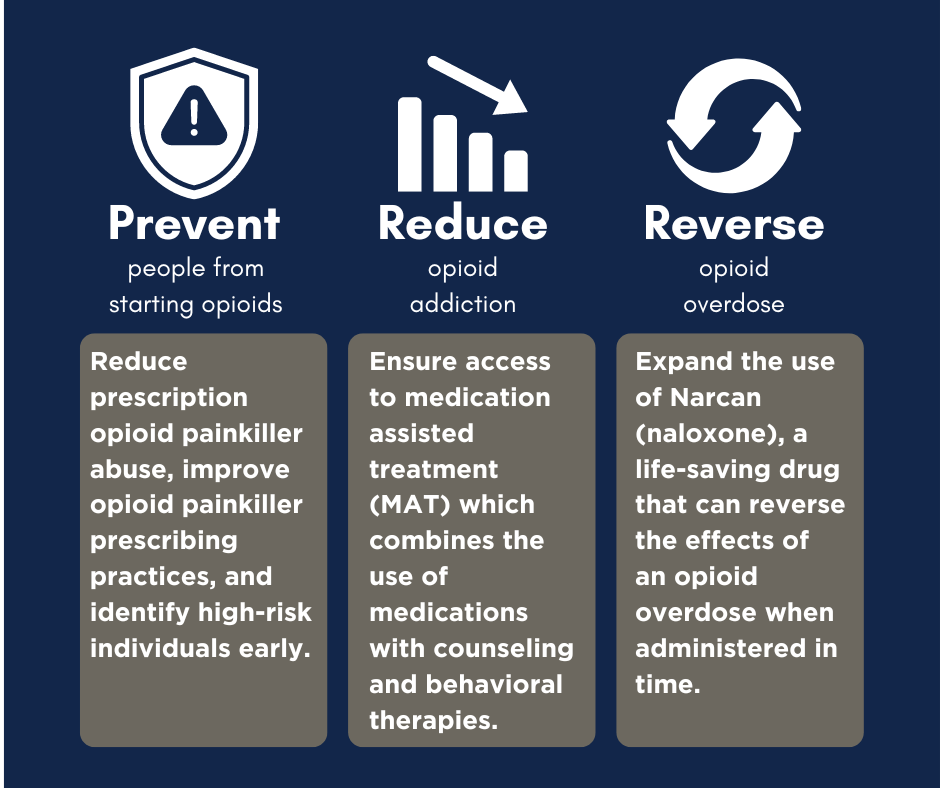
We must improve the way we treat pain in order to reverse the opioid epidemic, according to the CDC. Preventing substance abuse, addiction, and overdose before they occur is key to this process. In addition, increasing access to harm reduction programs and a variety of treatment options will work to reduce the rates of addiction and overdose fatalities.
This guide provides recommendations using the prevent, reduce, reverse framework from the CDC.
Opioids are a class of drugs used to reduce pain and include prescription opioids, synthetic opioids, and heroin. Prescription opioids have been widely accepted as the standard for pain management despite the risk of addiction and lack of evidence supporting their long-term effectiveness.
Commonly Prescribed Opioids
- Codeine
- Morphine
- Methadone
- Fentanyl
- Tramadol
- Oxycodone
- Bitatrate
- Hydrocodone
- Hydromorphone
- Oxymorphone
- Meperidine
- Propoxyphene

What is the difference between "tolerance." "dependence," and "addiction"?
Opioid tolerance is a reduced response to medication, requiring more opioids to experience the same effect.
Opioid dependence is when the body adjusts its normal functioning around regular opioid use.
Opioid addiction (Opioid Use Disorder) occurs when:
- attempts to cut down or control use are unsuccessful
- use results in social problems and a failure to fulfill obligations at work, school, and home
- it is physically challenging to stop opioid use
- there is an increased risk of withdrawal

The likelihood of developing an addiction differs from person to person, and no single factor determines whether a person will become addicted to drugs. In general, the more risk factors a person has, the greater the chance that taking drugs will lead to drug use adn addiction. Protective factors reduce a person's risk.
Risk Factors:
- aggressive behavior in childhood
- lack of parental supervision
- low peer refusal skills
- drug experimentation
- availability of drugs at school
- community poverty
Protective Factors:
- self-efficacy (belief in self-control)
- parental monitoring and support
- positive relationships
- good grades
- school anti-drug policies
- neighborhood resources
Oftentimes, people struggling with substance use will attempt to hide their symptoms. There are several common changes to look for if you are concerned that a loved one, friend, or co-worker is struggling.
Behavioral Changes:
- Drop in attendance or performance at work or school
- Frequently getting into trouble
- Engaging in secretive or suspicious behavior
- Changes in appetite or sleep
- Unexplained change in personality or attitude
- Sudden mood swings, irritability, or angry outbursts
- Periods of unusal hyperactivity, agitation, or giddiness
- Lack of motivation
- Appearing fearful, anxious, or paranoid
Physical Changes:
- Bloodshot eyes
- Abnormally sized pupils
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain
- Deterioration of physical appearance
- Unusual smells on breath, body, or clothing
- Tremors, slurred speech, or impaired coordination
Social Changes:
- Suden change in friends and hobbies
- Legal problems related to substance use
- Unexplained need for money or financial problems
- Using substances even though it causes problems in relationships
Opioid Overview







